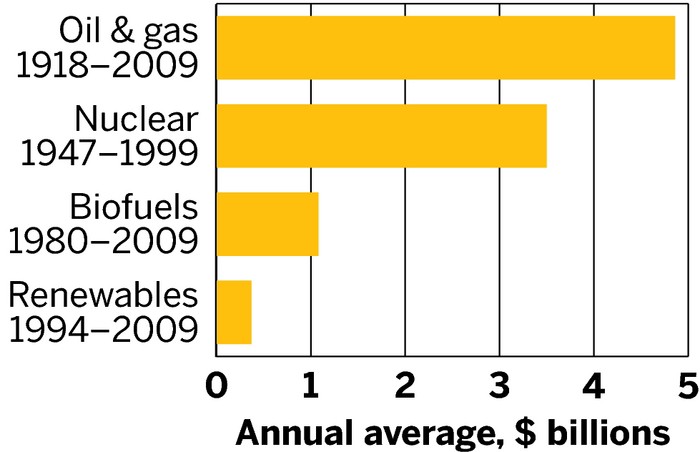
Tax subsidies have been used in all energy sectors over the last 50 years, these subsidies are used to promote the development and use of different energy sources, such as oil, gas, coal, nuclear, renewable, and alternative energy. The rationale behind these subsidies is to encourage investment, innovation, and expansion in the energy industry, which in turn can benefit the economy, the environment, and the society.
All Energy Sectors Have Benefited from Tax Subsidies
Over the past 50 years, the amount of tax subsidies used for all energy sectors has varied significantly depending on the political, economic, and social conditions of each country or region. In general, developed countries have tended to provide more subsidies for conventional energy sources, such as oil, gas, and coal, while developing countries have relied more on subsidies for renewable and alternative energy sources, such as wind, solar, biomass, and geothermal.
Tax Subsidies Reducing the Cost for Renewable Energy
According to a report by the International Energy Agency (IEA) published in 2020, global subsidies for fossil fuels, including tax subsidies, amounted to $478 billion in 2019, a slight decrease from $494 billion in 2018. These subsidies represent a significant burden on public finances and a barrier to the transition to cleaner and more sustainable energy systems. In contrast, subsidies for renewable energy, including tax incentives, amounted to $135 billion in 2019, a slight increase from $132 billion in 2018. These subsidies have played a crucial role in the rapid growth and cost reduction of renewable energy technologies, such as solar photovoltaics (PV) and wind turbines.
Fossil Fuel Dependence Exposed Geopolitical Risk
The IEA report also highlights the need for a phase-out of fossil fuel subsidies and a shift towards more targeted and transparent support for low-carbon energy technologies. This approach would not only reduce the negative environmental and health impacts of fossil fuels but also create new opportunities for job creation, innovation, and social development. Moreover, the COVID-19 pandemic has exposed the vulnerability of fossil fuel-dependent economies to market shocks and geopolitical risks, reinforcing the case for a diversified and resilient energy system.
Tax Subsidies Shifting From Fossil Fuel Support to Renewables
In the United States, tax subsidies for energy have been a contentious issue for decades, with different political parties and interest groups advocating for different policies and priorities. According to a report by the Congressional Research Service (CRS) published in 2021, federal tax expenditures for energy totaled $17.6 billion in fiscal year 2019, representing 0.8% of all federal tax expenditures. The majority of these expenditures went to renewable energy sources, such as the investment tax credit (ITC) and the production tax credit (PTC) for solar and wind energy, which amounted to $5.7 billion and $4.5 billion, respectively. Other tax expenditures for energy included incentives for oil and gas exploration, production, and refining, as well as for nuclear energy, biofuels, and alternative vehicles.
The Changing Landscape
The CRS report also notes that tax expenditures for energy have been subject to frequent changes and extensions, often depending on the political and economic priorities of the Congress and the Administration. For example, the ITC and PTC for solar and wind energy have been extended multiple times, with varying durations and phasing-out schedules, to encourage continued growth and investment in these industries. Similarly, tax incentives for oil and gas have been modified to reflect changing market conditions and environmental regulations, such as the elimination of certain tax breaks for shale gas and the introduction of tax credits for carbon capture and storage (CCS).
Throughout the last 50 years and beyond tax incentives and other subsides have supported all energy sectors. Given the climate concerns throughout the world more of these subsidies are being directed toward clean and renewable energy sectors. The hope of these efforts is to support more reliance on clean energy and less dependency on Fossil Fuels. In the end it should support a world where countries have more energy independence.