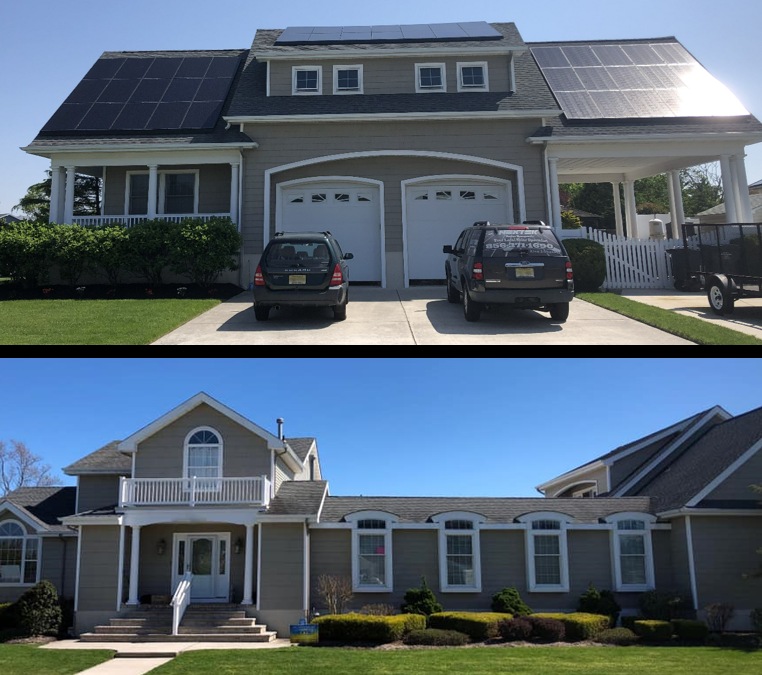
The state of Massachusetts offers many incentives for a solar system. The federal tax credit, the net metering policy, and solar rebates are just some of the incentives available to you. However, there are also a number of laws and regulations that must be followed before you can install a solar system in your home. Luckily, this guide will help you understand what they are and what you need to know before you make the leap.
Solar energy is a great way to save money. It not only reduces your monthly electricity bill, but it also helps you support the local economy. In addition, a solar PV system has a 30-year life expectancy. This means that your system is producing money long after you pay for the initial installation.
There are two primary solar options, one being the ownership model and the second being the no upfront cost PPA or Lease model. Each is designed to save money and provide predictable longterm energy savings. It’s fair to say that either option helps reduce your monthly electric bill and decrease your dependency on the high cost of electricity provided by your present electric company.
When you are considering going solar, you may be wondering how the costs compare to the national average. In general, a solar panel system in Massachusetts will cost about $3 to $5 per watt. That means that a 5-kilowatt solar PV system can cover about 80% of the typical New England house-hold’s electricity usage.
In addition, the state of Massachusetts offers a property tax exemption on the value of your solar panel system. For the first 20 years, your property taxes will be completely exempt.
The state of Massachusetts has recently reaffirmed its commitment to net metering for residential solar systems. Net metering allows you to sell excess energy to your utility.